Bypassing passwords with man-in-the-middle
Man-in-the-middle is a type of attack used by spy organizations and professional criminals alike to bypass passwords, steal login information, record private messages, move funds… Essentially, man-in-the-middle attacks can have an effect on any aspect of web-traffic. They are invisible and very difficult to detect.
How it works:
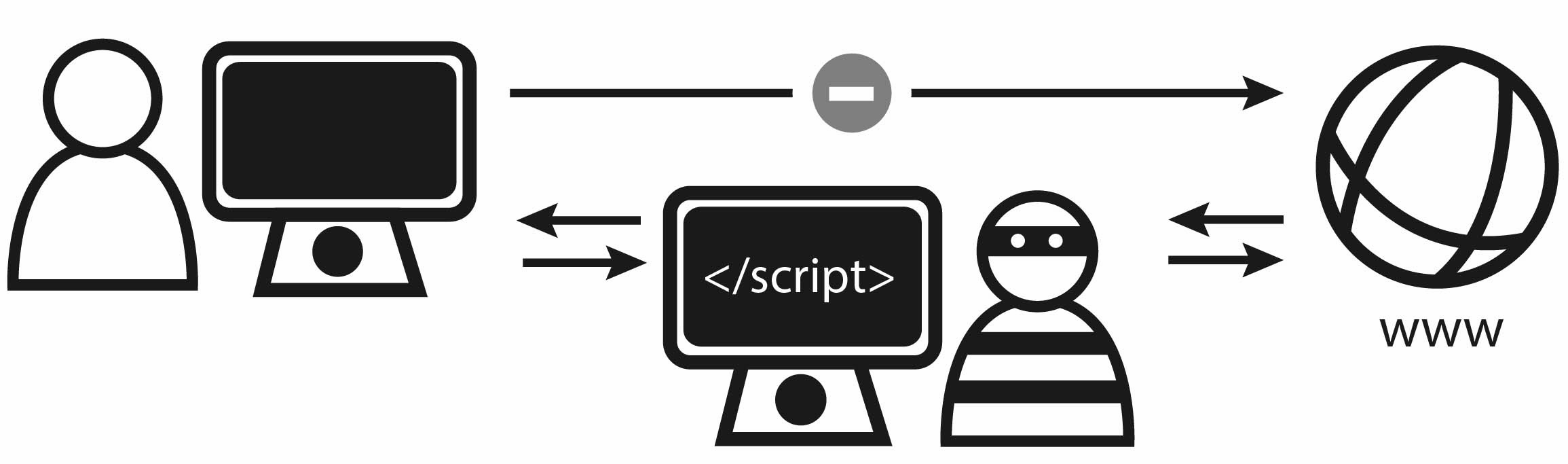
Normal web traffic should flow from a user’s computer (Point A) to a web app or service (Point B). The response then flows back. Man-in-the-middle attacks exploit the space between those points to gather sensitive information.
Man-in-the-middle attacks cause traffic to flow from Point A, through Fraudster X to Point B.
Traditionally it is achieved by someone connected to the same network as their victim, re-routing traffic. However, there are some more advanced methods which we’ll talk about later. Firstly,
What can someone in the middle do?
- Sniff traffic: Listen for and steal data travelling to-and-from a device
- Alter traffic: Change messages or commands which are in transit
Take a look at this example:
4 Stages of MITM: User sends gift money to a relative online
1. Legitimate Action
- User logs into online bank
- Enters $500.00 transfer to account number 12345678
- Clicks Send
2. Sniff + Alter
- Man-in-the-middle sniffs login details for future use
- Changes transfer to $5,000 and account number to 98765432
3. Process Transaction
- Bank receives and processes altered command
- Bank returns a confirmation with new account balance
4. Fraud Complete
- Man-in-the-middle changes response to the expected account balance.
This should give you some idea of why public Wi-Fi access points are considered so dangerous.
How easy is it?
It can be very easy. Free to download software can turn any laptop into a “man-in-the-middle” ready to attack anybody on the same network. A quick YouTube search for ‘steal login cookies’ will get you up to speed in fewer than 10 minutes. Login cookies are what remember you are logged into online banking or social networks, stealing them is a free pass to a user’s account.
Advanced Attacks
- Evil-twin networks. Making a Wi-Fi network that looks identical to the victim’s home or office network. Devices mistakenly auto-connect, the evil-twin may steal their information or simply record messages, unnoticed.
- Malware: Once installed, it routes web-traffic through another location, a remote version of man-in-the-middle known as man-in-the-browser.
Who is at risk?
MITM is either targeted to specific individuals or groups such as employees of a target company or automated using customized malware.
High profile individuals are more at risk of targeted attacks. Company executives, politicians, celebrities, employees of notable firms. By contrast, high profile websites – e-commerce sites, social networks, webmail providers, online banks. – are considered high risk for attacks employing MITM malware.
Protection
Because man-in-the-middle is so hard to detect, protection against attacks should be layered, including defenses by the user who sends the traffic and by the web-service or company who processes data and replies.